 Hire a Tutor
Hire a Tutor 





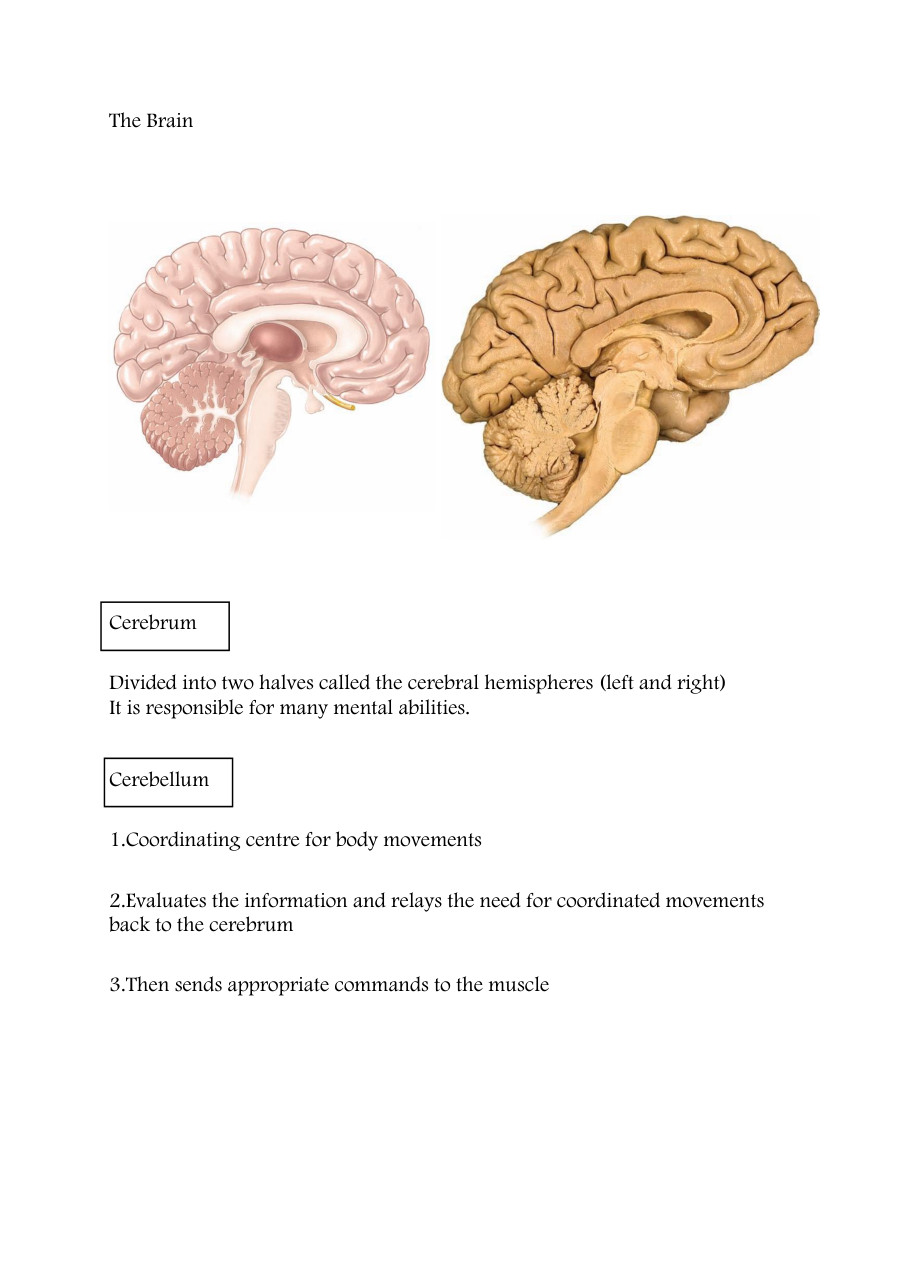

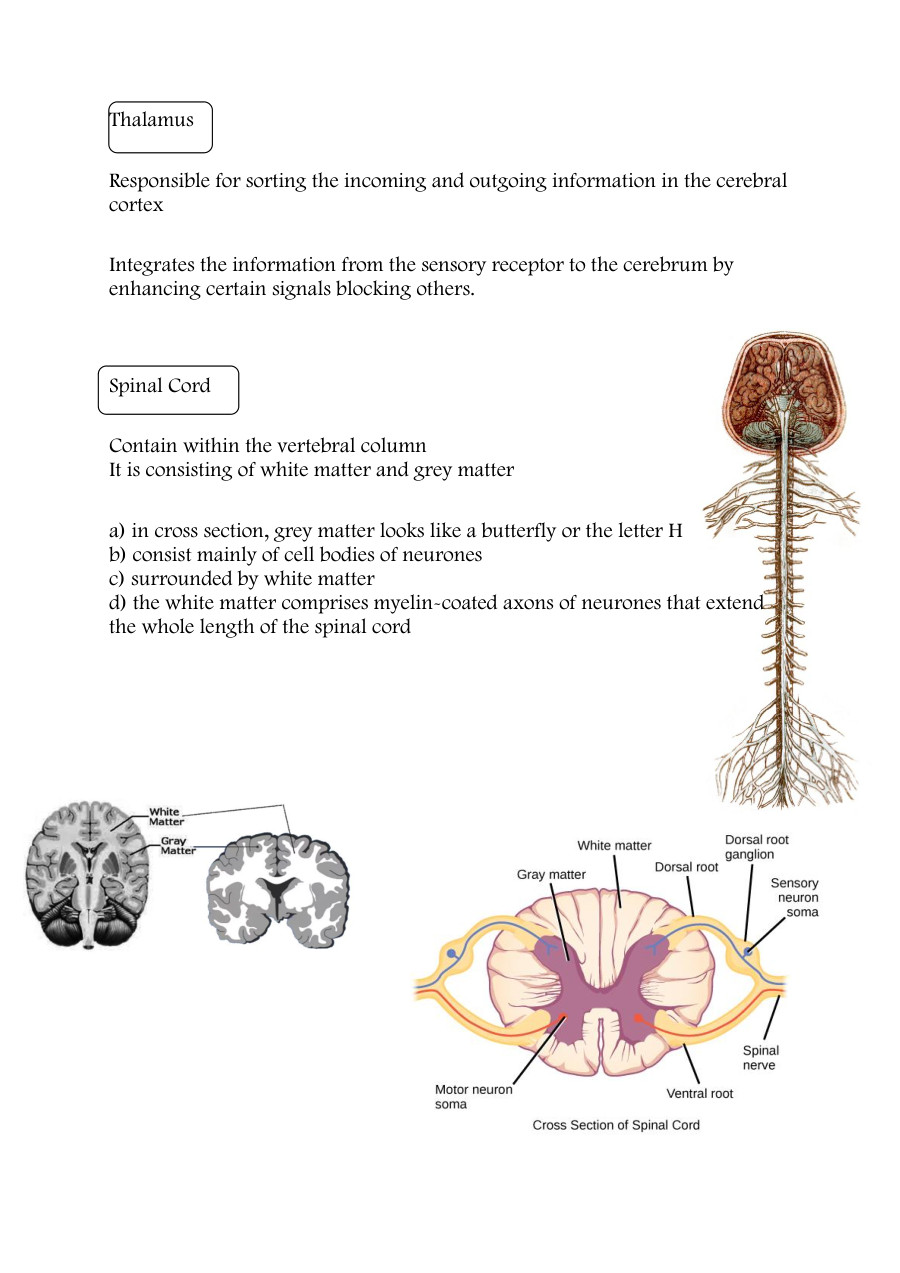

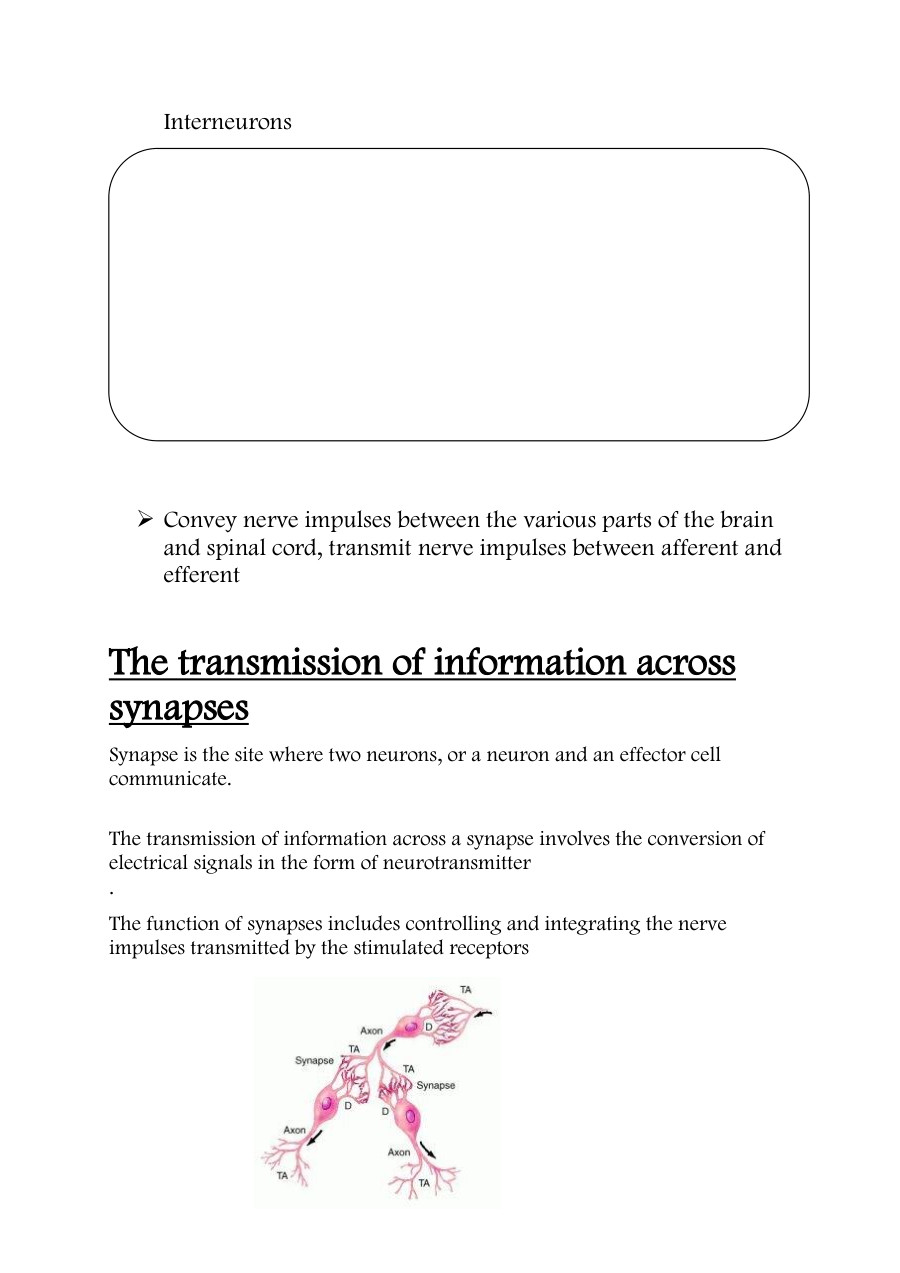

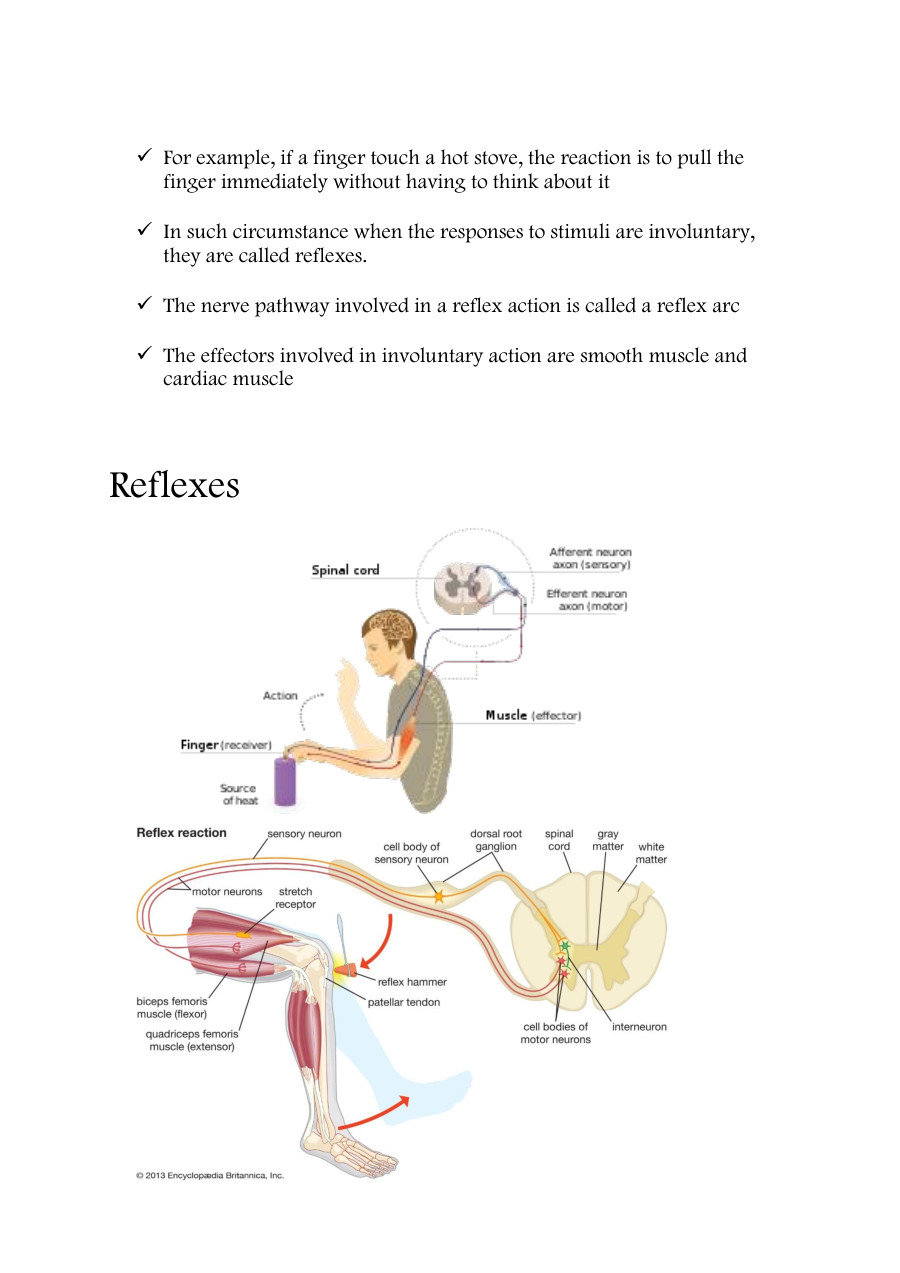


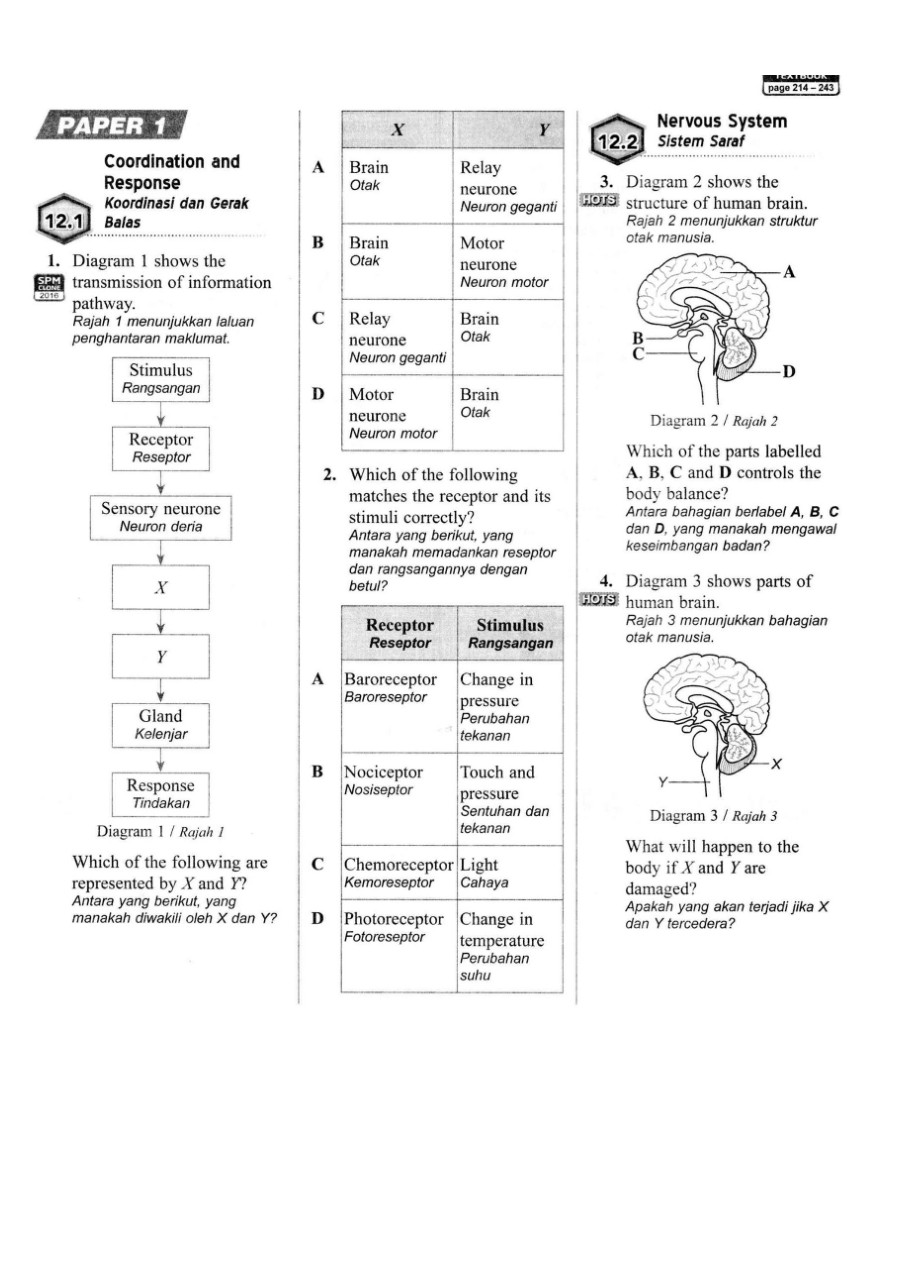

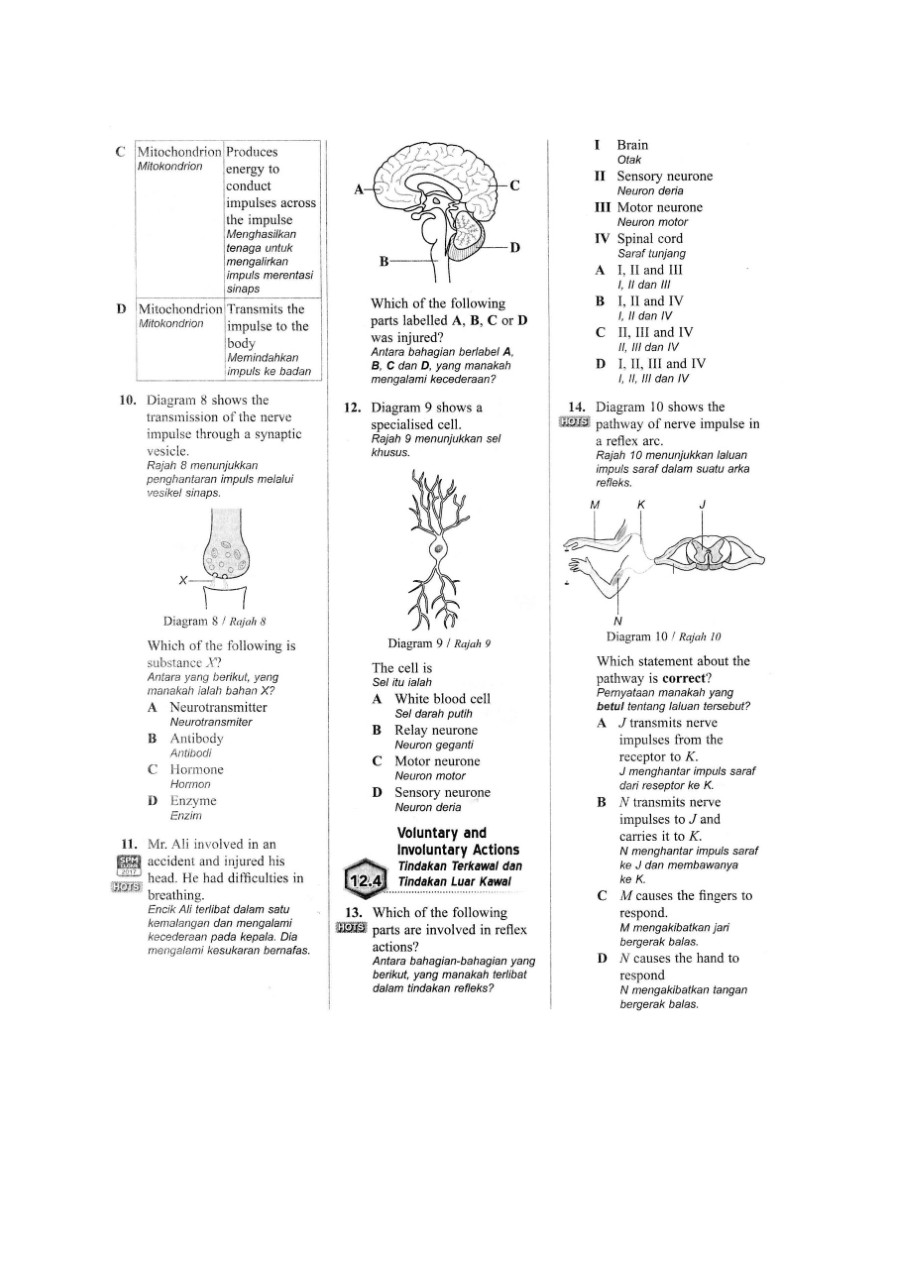





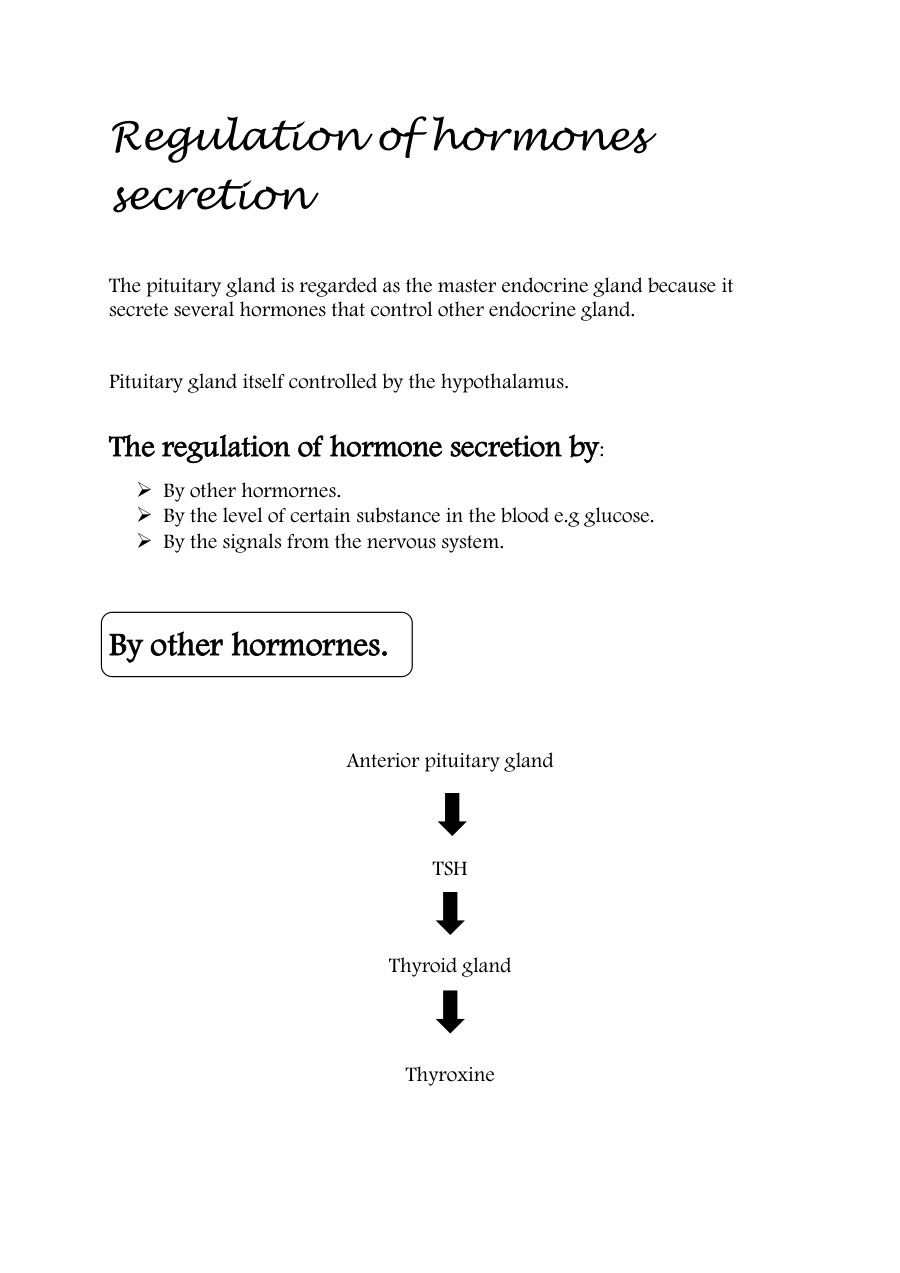
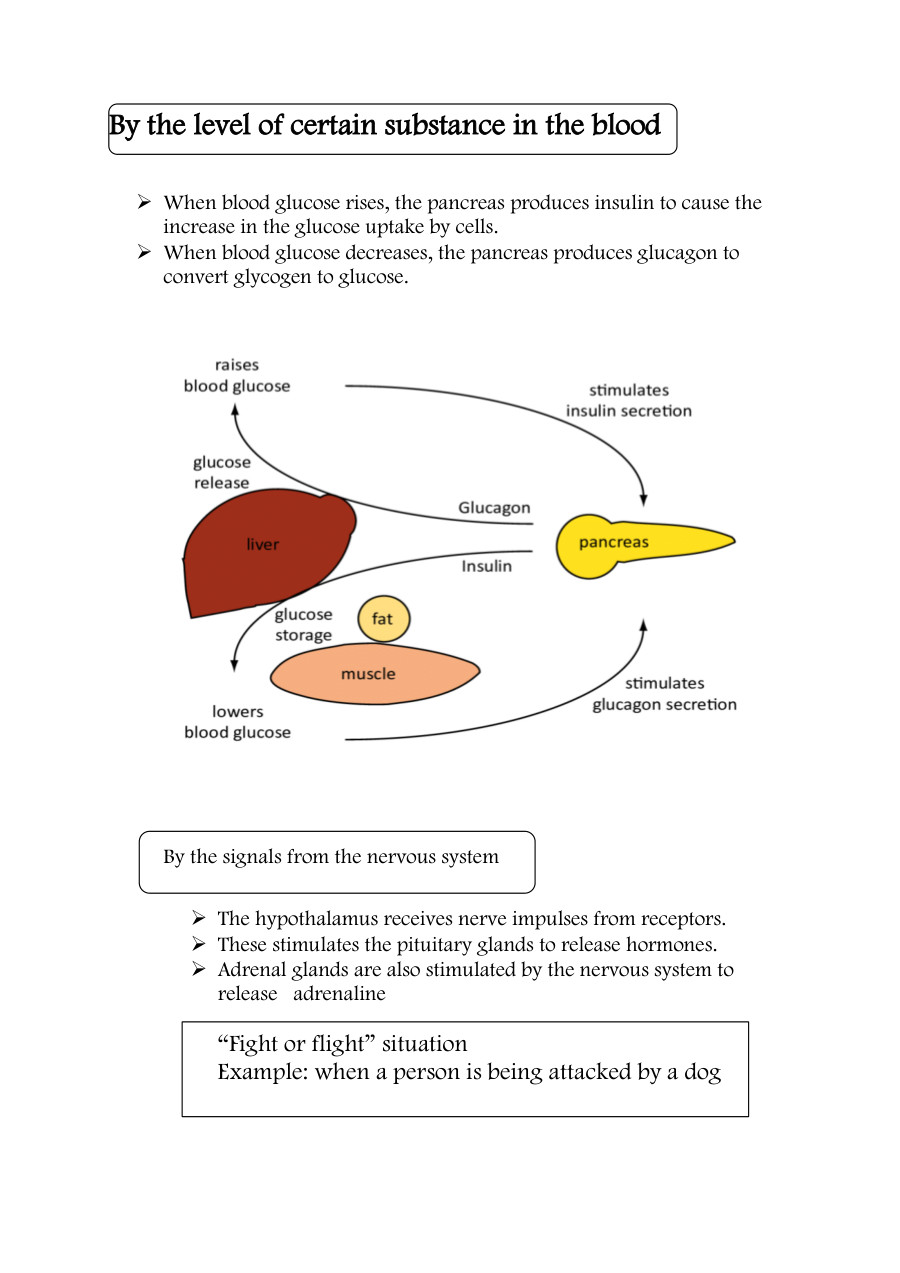







Organisms respond to changes in the internal or external environment (stimuli) for survival. There are two types of response: chemical and nervous. The nervous system allows the body to respond to stimuli in the internal and external environment and is coordinated by the brain and / or spinal cord.
7 years of teaching experience
Qualification: B.Sc (Forensic)(Hons), USM
Teaches: English, Science, Biology, Chemistry
