 Hire a Tutor
Hire a Tutor 




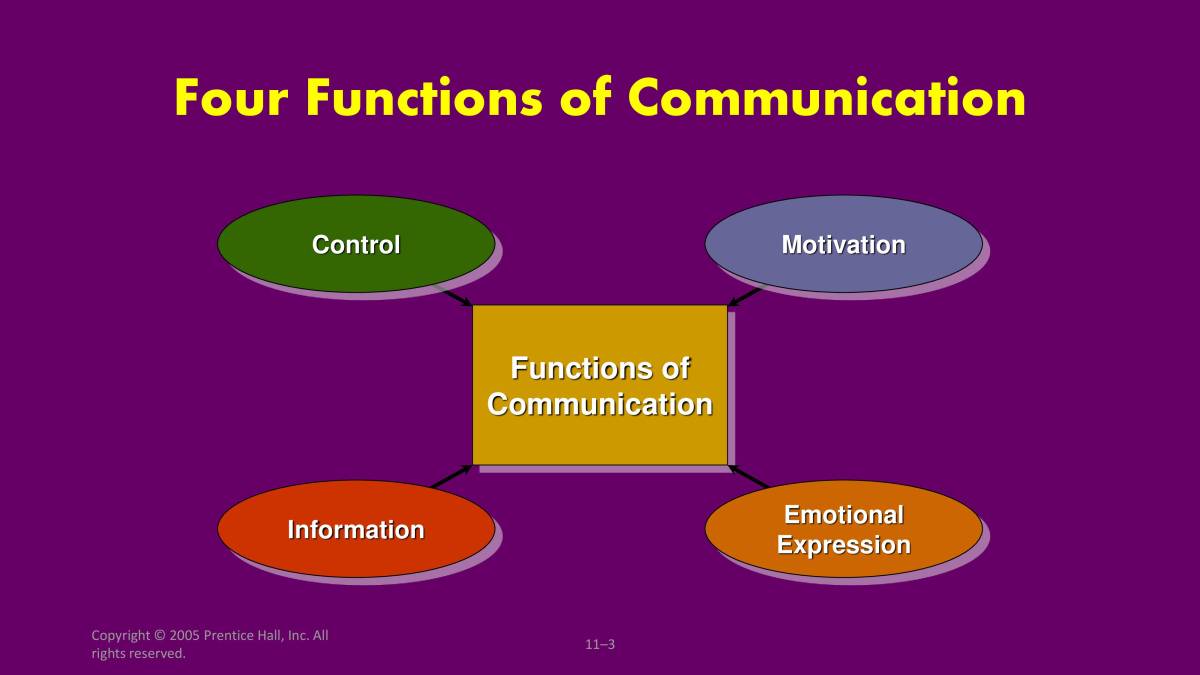


















This PPT will give a very handful knowledge about communication. There is various kind of communications like Interpersonal Communication,Organizational Communication etc.This Ppt will also give a brief idea about various functions of communication.
10 years of teaching experience
Qualification: MBA Strategic Management
Teaches: Business Studies, Presentation Skills, Public Speaking, Resume Writing, English, Bahasa Melayu, Economics, Management
